Stainless steel 21-6-9 - AMS 5561 - Nitronic 40 - S21900 - X2CrMnNi21-6-9 - Z4CMN 21-9-6
21-6-9, also known as AMS 5561, UNS S21900, or Nitronic 40, is an austenitic stainless steel alloy strengthened with nitrogen. This enhancement provides superior corrosion resistance compared to standard 300-series steels, excellent toughness (a characteristic of austenitic alloys), and high mechanical strength. Its ability to withstand cryogenic temperatures makes it highly sought after for aerospace applications.
Available shapes :
Order 21-09-06 Online
Select the desired form, standard, or specification and place your order with one click. A member of our sales team will contact you promptly to finalize your order.
General Introduction to 21-6-9
Thanks to its high chromium content, this steel resists oxidation and corrosion even under aggressive conditions such as intergranular corrosion. Its reinforcement with manganese and nitrogen increases the strength and stability of the austenite and gives it excellent toughness, which it retains down to temperatures close to those of liquid helium (-269 °C or -516 °F).
The 21-6-9 alloy does not respond to heat treatments for hardening by quenching, tempering, or aging, unlike martensitic steels. On one hand, it does not contain enough aluminum, titanium, or copper to allow for age hardening. On the other, its austenite is too stable at low temperatures for quenching or tempering to be effective. However, cold working to increase hardness is possible—or hot working to improve ductility—without degrading the material.
Hot Working, Cold Working
21-6-9 stainless steel should be hot worked in a temperature range between 927 °C and 1204 °C (1700–2200 °F). Maintaining a controlled temperature is essential to avoid damaging the material’s microstructure.
- Heat the alloy evenly to ensure uniform deformation.
- Cool rapidly to room temperature (water or air) to preserve mechanical properties.
Serve while it's hot.
Cold working includes rolling, drawing, and stamping at room temperature. Due to its high work hardening rate, 21-6-9 requires higher forming forces than other austenitic stainless steels (such as 302, 304, and 316). An intermediate anneal is necessary to reduce hardness and facilitate further cold working. This process (cold work → anneal → further cold work) significantly increases its yield strength.
Mechanical and Chemical Properties
When hardened (work hardened), 21-6-9 has a yield strength of at least 827 MPa, ensuring durability under heavy loads. Its tensile strength can reach 1117 MPa. Its elongation capability is at least 35 % in the annealed state, and it maintains at least 20 % elongation when hardened.
This alloy remains non-magnetic even after severe cold working, an important characteristic of Nitronic grades (unlike 301/304 steels, which can become slightly magnetic after work hardening due to martensite formation). The austenite in 21-6-9 is very stable.
Machinability, Formability
Because of its high work hardening rate, 21-6-9 is more difficult to machine than most austenitic stainless steels. Similar to type 316, it is recommended to use slow cutting speeds, positive feeds, and ample cutting fluids.
It offers good formability and handling in the annealed condition. However, its high yield strength and work hardening rate require greater forces during forming than other steels like 304L. Techniques such as bending, drawing, and stretching can be applied, but an intermediate anneal may be necessary to prevent cracking and ensure uniform deformation.
Weldability
21-6-9 is considered to have good weldability. Several welding methods can be successfully applied:
- TIG welding produces precise welds. An inert gas such as argon or helium protects the weld zone.
- MIG welding offers high deposition rates.
- SMAW (shielded metal arc welding) is also suitable. A complete post-weld anneal is recommended to reduce residual stresses and restore corrosion resistance.
Oxy-acetylene welding should be avoided, as it risks carbon buildup that would compromise the material’s properties.
Industrial applications
In addition to the aerospace industry, the 21-6-9 alloy is also used for:
- Cryogenic applications: tanks, piping, valves, and fittings for cryogenic storage and transport vessels (LNG, liquid nitrogen, liquid helium)
- Chemical and petrochemical processing: pressure vessels and reactors
- Marine applications: propeller shafts for boats and ships
- Automotive (high-performance / specialized)
- Nuclear
Chemical composition of 21-09-06
The variations in its chemical composition for aerospace.
| % | C Carbon | Cr Chromium | Cu Copper | Mn Manganese | Mo Molybdenum | N Nitrogen | Ni Nickel | P Phosphorus | S Sulfur | Si Silicon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | <0.00 | 19.00 | <0.00 | 8.00 | <0.00 | 0.15 | 5.50 | <0.00 | <0.00 | <0.00 |
| Max. | 0.04 | 21.50 | 0.75 | 10.00 | 0.75 | 0.40 | 7.50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.00 |
Related stainless steel alloys
15-5PH, 1.4545, X5CrNiCu15-5, EZ5CNU15.15
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, PROFILE, SHEET
17-4PH, 1.4548, UNS S17400, AMS 5643, AMS 5622, S17400
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET
17-7PH, S17700, 1.4568, AISI 631, X7CrNiAl17-7
SHEET
AISI 301, Z12CN18-07, X12CrNi17-7, X10CrNi18-8
MOTHER COIL, COIL, SHEET
AISI 302, Z12CN18-09
SHEET
AISI 347, X6CrNiNb18-10, Z6CNNb18-11
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET, ROUND TUBE
AISI 431, X17CrNi16-2, Z15CN16-02, FE PM42, 1.4057, APX
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET
AISI 446
ROUND BAR
CALE PELABLE
SHEET
CUSTOM 465, MLX17, X1CrNiMoAlTi12-11
ROUND BAR
EZ100CD17
ROUND BAR
EZ12CNDV12
ROUND BAR
EZ15CN17-03
ROUND BAR
EZ1CNDAT12-09, MARVALX12, X1CrNiMoAlTi12-9
ROUND BAR
EZ2NKD18-8-5, MARAGING 250, X2NiCoMo18-8-5
RECTANGULAR BAR
EZ3NCT25, X3NiCrTi25
ROUND BAR, COIL, SHEET (THICKNESS > 6MM)
EZ6CND16-05-01
SQUARE BAR
EZ6NCT25, A286, X6NiCrTi25
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, WIRE, SHEET
EZ8CND17-04
ROUND BAR
GD223, X50NiMnCr12, Z50NMC12
ROUND BAR
PH13-8Mo, X3CrNiMoAl13-08-02, Z3CND13-08
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR
S130
ROUND BAR
S143
ROUND BAR
S143D
ROUND BAR
S144
ROUND BAR
S145
ROUND BAR
X12C13, X12Cr13, AISI 410, 1.4006, Z10C13
ROUND BAR, SHEET
X30Cr13, Z30C13
ROUND BAR
X6Cr17
ROUND BAR
X750
SHEET
Z100CD17
ROUND BAR
Z12CN13
SHEET
Z12CNDV12, JETHETE M152, X12CrNiMoV12
ROUND BAR, SHEET
Z25CNWS22
ROUND BAR
Z2CN18-10, AISI 304L, X1CrNi18-10
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, WIRE, PROFILE, SHEET, PERFORATED SHEET, PVC SHEET, ROUND TUBE
Z6CND16-05-01, APX4, Z8CND17-04, X4CrNiMo16-5-1
ROUND BAR, SHEET
Z6CNT18-10, AISI 321, X6CrNiTi18-10, X6CNT18-10
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, SHEET, ROUND TUBE
Key properties
The most remarkable properties of this stainless steel alloy
Reduction of Area Z
73.638–79.167 %
Tensile Strength
690–1117 MPa
Impact Toughness
115.2–325.3 J
Yield Strength
≥ 386.4 MPa
How 21-09-06 is used in aerospace
The practical applications of this stainless steel in aircraft construction.
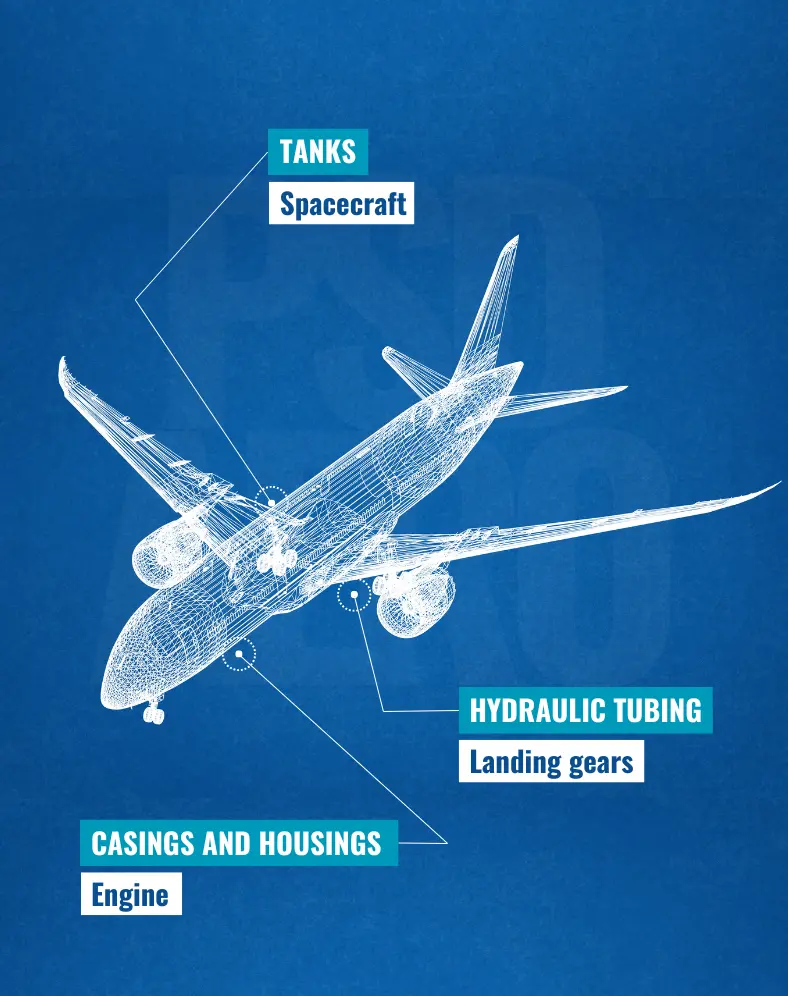
Cryogenic tanks and lines
A key application area for 21-6-9, used in liquid-fueled rockets.
Casings and housings
21-6-9 is used in compressor casings or engine exhaust systems for its good fatigue and corrosion resistance, as well as its formability.
Hydraulic tubing
Another major application of 21-6-9 is in the aircraft's hydraulic system, including fittings, for example, and components of the landing gear.









