Stainless steel AISI 431 - X17CrNi16-2 - Z15CN16-02 - FE PM42 - 1.4057 - APX
The martensitic stainless steel AISI 431 is a high-strength chromium–nickel stainless grade with good mechanical properties. It also offers good corrosion resistance — the best among all martensitic stainless steels — largely due to the nickel in its composition. It is therefore well suited to highly stressed components (shafts, axles, etc.) when used in the quenched and tempered condition with a carefully finished surface.
Available shapes :
Order AISI 431 Online
Select the desired form, standard, or specification and place your order with one click. A member of our sales team will contact you promptly to finalize your order.
A nickel-alloyed martensitic steel
Martensitic stainless steels are a distinct type of ... These steels are mainly alloyed with chromium and carbon.
Role and benefits of nickel in its composition
AISI 431 contains between 1.5 and 2.5% nickel. The presence ... nickel in AISI 431 improves corrosion resistance by widening the austenitic domain at high ... temperature. This makes it possible to increase the chromium content without reducing its toughness or its corrosion resistance. The alloy therefore offers better performance in environments prone to localized corrosion, such as marine or moderately acidic conditions.
Nickel also contributes to the toughness of martensitic steel ... which makes it more resistant to mechanical stresses.
Finally, its high chromium content forms a robust ... in marine environments where salt water can be particularly aggressive.
Heat treatment and its influence on properties
The heat-treatment process includes three steps ... to reduce brittleness while maintaining hardness).
Quenching and tempering process
- Austenitizing must be carried out at temperatures ... between 980 °C and 1065 °C, transforming the steel structure into austenite.
- It is followed by an air or oil quench to cool ... which rather requires an oil quench to avoid the formation of softer phases.
- Tempering between 370 °C and 565 °C must be avoided ... to the detriment of toughness and corrosion resistance.
Chart 1 – Ductility and toughness vs tempering temperature
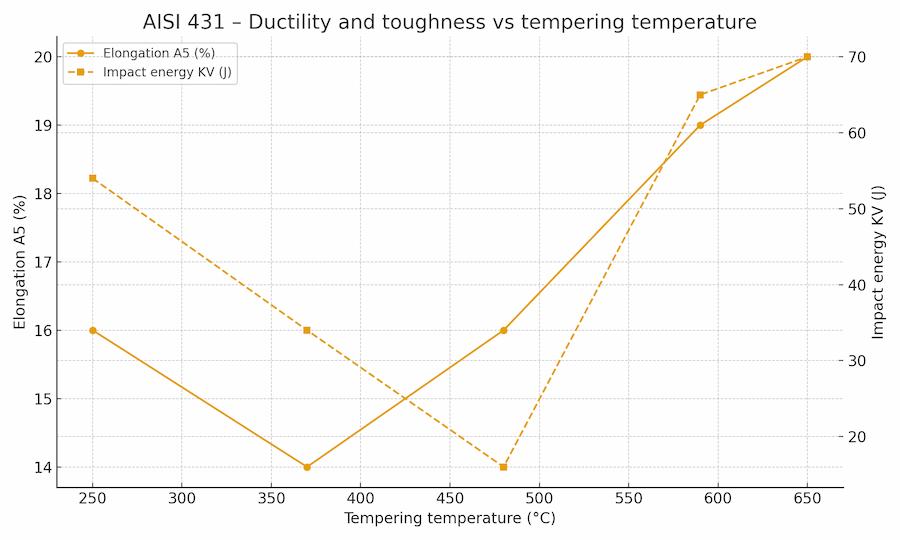
On this second chart, it can be seen that intermediate tempers (≈ 370–480 °C) cause a sharp drop in impact energy without any real gain in ductility: this is the temper embrittlement zone to avoid. High tempers (590–650 °C), on the other hand, restore good ductility and high toughness, offering the best compromise for shafts and critical parts.
Chart 2 – Strength and hardness vs tempering temperature
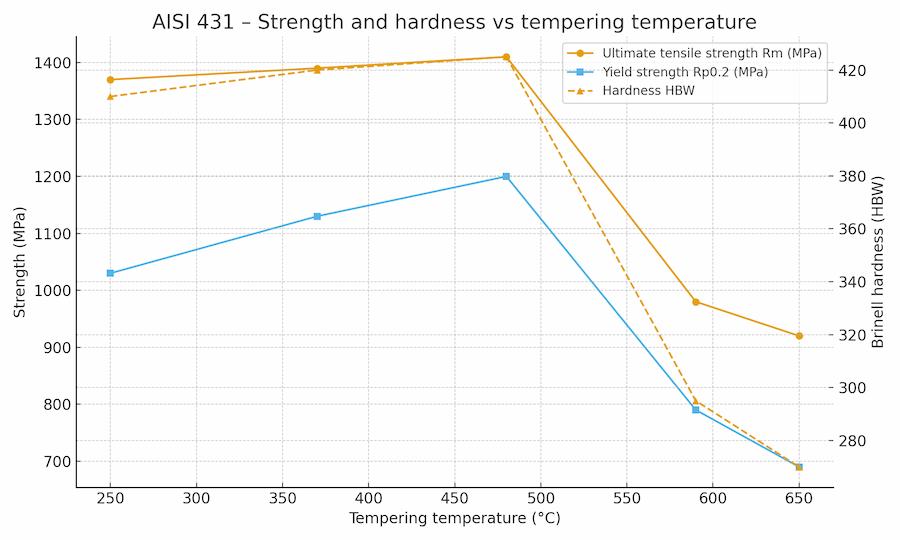
As shown on this chart, AISI 431 retains a ... high ... better suited to highly loaded structural parts.
Mechanical properties depending on delivery condition
In general, the yield strength of AISI 431 is at least 600 MPa, and its tensile strength is between 800 and 1050 MPa. Its minimum elongation is 10%, and its hardness ranges between 229 and 440 HB.
Detailed table of AISI 431 mechanical properties
EN condition | Diameter d (mm) | Rp0.2 min (MPa) | Rm (MPa) | A5 min (%) | KV2 min (J) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
+A (annealed) | – | – | ≤ 950 | – | – | Soft condition, not used for strength |
+QT800 | d ≤ 60 | 600 | 800 – 950 | 14 | 25 | Quenched and tempered martensite, balance of Rm/A/KV |
+QT800 | 60 < d ≤ 160 | 600 | 800 – 950 | 12 | 20 | Slightly lower properties on large diameters |
+QT900 | d ≤ 60 | 700 | 900 – 1050 | 12 | 16 | Higher strength, lower ductility |
+QT900 | 60 < d ≤ 160 | 700 | 900 – 1050 | 10 | 15 | High-strength variant for large sections |
This table shows the classic strength / duc... as the tensile strength increases, the elongation A5 and the impact energy KV2 decrease.
Welding, forging, machining, and polishing behavior
AISI 431 is difficult to weld and precautions ... must be taken. A gas containing hydrogen or nitrogen must never be used for welding ... this grade. Preheating between 200 and 300 °C is required and, during welding, the alloy must not cool below 200 °C.
AISI 431 has average forgeability: during ... the forging process, the material must first be heated slowly to 850 °C, then quickly to 1180 °C. ... can be performed between about 950 and 1150 °C. The material must then be cooled slowly, preferably in ... a furnace or dry sand. It is widely used for shafts, bolts, and valve parts, which are frequently produced by die forging or open-die forging.
Finally, it has very good polishing capability and ... and poor machinability. It is “ gummy ” in the annealed condition and hard in the quenched condition. It is prone to galling and its ... machinability is comparable to that of 304 but clearly inferior to that of a sulfurized stainless steel such as 416.
Corrosion behavior
AISI 431 is one of the best-performing martensitic stainless ... provided it is machined correctly and, ideally, polished and passivated.
In chloride environments, the point to watch is pitting corrosion ... and you may need to switch to 316L, duplex, or a more highly alloyed PH stainless steel.
Overall, corrosion resistance depends strongly ... on heat treatment (especially at grain boundaries and in welded HAZs).
In the presence of H2S or acidic environments (oil ... and gas), 431 has limitations: it may be suitable for secondary parts in mildly aggressive areas, but grades ... specifically qualified to NACE (13Cr, duplex, nickel alloys) are preferred for pressurized parts.
Industrial applications
Aerospace industry : this stainless steel ... is highly valued by the aerospace industry due to its exceptional tensile strength, toughness ... and corrosion resistance. These properties make it suitable for critical components such as cold-section parts ... turbine parts and fasteners that must withstand high stresses and harsh environmental conditions.
Marine industry : marine fasteners, propeller shafts (its main application), and pump components.
Automotive industry : gears and fuel injection components.
Chemical composition of AISI 431
The variations in its chemical composition for aerospace.
| % | C Carbon | Cr Chromium | Mn Manganese | Ni Nickel | P Phosphorus | S Sulfur | Si Silicon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | 0.12 | 15.00 | <0.00 | 2.00 | <0.00 | <0.00 | <0.00 |
| Max. | 0.20 | 18.00 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 0.035 | 0.025 | 1.00 |
Related stainless steel alloys
15-5PH, 1.4545, X5CrNiCu15-5, EZ5CNU15.15
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, PROFILE, SHEET
17-4PH, 1.4548, UNS S17400, AMS 5643, AMS 5622, S17400
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET
17-7PH, S17700, 1.4568, AISI 631, X7CrNiAl17-7
SHEET
21-09-06, AMS 5561, Nitronic 40, S21900, X2CrMnNi21-6-9, Z4CMN 21-9-6
ROUND TUBE
AISI 301, Z12CN18-07, X12CrNi17-7, X10CrNi18-8
MOTHER COIL, COIL, SHEET
AISI 302, Z12CN18-09
SHEET
AISI 347, X6CrNiNb18-10, Z6CNNb18-11
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET, ROUND TUBE
AISI 446
ROUND BAR
CALE PELABLE
SHEET
CUSTOM 465, MLX17, X1CrNiMoAlTi12-11
ROUND BAR
EZ100CD17
ROUND BAR
EZ12CNDV12
ROUND BAR
EZ15CN17-03
ROUND BAR
EZ1CNDAT12-09, MARVALX12, X1CrNiMoAlTi12-9
ROUND BAR
EZ2NKD18-8-5, MARAGING 250, X2NiCoMo18-8-5
RECTANGULAR BAR
EZ3NCT25, X3NiCrTi25
ROUND BAR, COIL, SHEET (THICKNESS > 6MM)
EZ6CND16-05-01
SQUARE BAR
EZ6NCT25, A286, X6NiCrTi25
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, WIRE, SHEET
EZ8CND17-04
ROUND BAR
GD223, X50NiMnCr12, Z50NMC12
ROUND BAR
PH13-8Mo, X3CrNiMoAl13-08-02, Z3CND13-08
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR
S130
ROUND BAR
S143
ROUND BAR
S143D
ROUND BAR
S144
ROUND BAR
S145
ROUND BAR
X12C13, X12Cr13, AISI 410, 1.4006, Z10C13
ROUND BAR, SHEET
X30Cr13, Z30C13
ROUND BAR
X6Cr17
ROUND BAR
X750
SHEET
Z100CD17
ROUND BAR
Z12CN13
SHEET
Z12CNDV12, JETHETE M152, X12CrNiMoV12
ROUND BAR, SHEET
Z25CNWS22
ROUND BAR
Z2CN18-10, AISI 304L, X1CrNi18-10
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, WIRE, PROFILE, SHEET, PERFORATED SHEET, PVC SHEET, ROUND TUBE
Z6CND16-05-01, APX4, Z8CND17-04, X4CrNiMo16-5-1
ROUND BAR, SHEET
Z6CNT18-10, AISI 321, X6CrNiTi18-10, X6CNT18-10
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, SHEET, ROUND TUBE
Key properties
The most remarkable properties of this stainless steel alloy
Ductility
≥ 10%
Tensile Strength
725–965 MPa
Yield Strength
≥ 620 MPa
Brinell Hardness
229–440 HB



