Stainless steel 15-5PH - 1.4545 - X5CrNiCu15-5 - EZ5CNU15.15
Stainless steel 15-5 PH is a martensitic precipitation-hardening alloy, characterized by high mechanical strength and good corrosion resistance. Derived from the 17-4 PH grade, of which it is an evolution, 15-5 PH features a more homogeneous microstructure and improved toughness.
Explore a comprehensive overview of 15-5 PH, covering its key properties, applicable heat treatments, aspects related to forming and machining, as well as its typical applications.
Available shapes :
Order 15-5PH Online
Select the desired form, standard, or specification and place your order with one click. A member of our sales team will contact you promptly to finalize your order.
15-5 PH Stainless Steel: Properties, Heat Treatment, and Applications
15-5 PH stainless steel is a precipitation-hardenable alloy featuring a martensitic structure. It is designed to provide both excellent corrosion resistance and very high mechanical strength. It results from efforts to improve another well-known grade: 17-4 PH. Compared to the latter, it has a more homogeneous microstructure and better toughness.
Its name can be broken down as follows: approximately 15% chromium and 5% nickel are included in its composition (with the possible addition of copper), and the abbreviation “PH” stands for “Precipitation Hardening” (precipitation hardening).
Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties
The hardness of the martensitic phase in 15-5 PH is enhanced by the precipitation of fine particles during heat treatment. This dual characteristic gives it high mechanical strength even at temperatures up to around 315 °C. Its main mechanical properties are detailed below
Regarding its corrosion resistance, it performs best in the fully hardened state, nearly matching that of 17-4 PH. Among all martensitic steels, it offers the best corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. Nonetheless, they are generally less resistant to corrosion than duplex (austenitic-ferritic) steels.
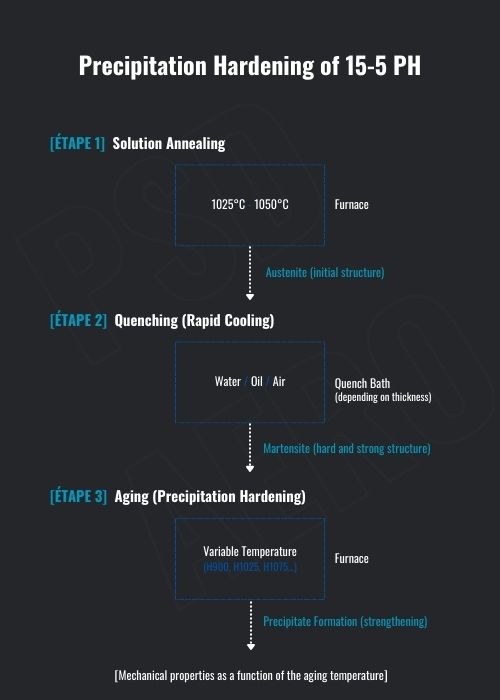
Heat Treatment
15-5 PH can be precipitation-hardened, and here is the process:
- The process begins with an initial heating (solution annealing) between 1025 °C and 1050 °C
- Followed by a rapid cooling (in water, oil, or air depending on the thickness of the piece). This quenching transforms austenite into martensite, which is harder and stronger.
- Next, a second heating (aging) is carried out at a lower temperature to allow the formation of precipitates within the metal, further increasing its hardness and strength.
- Finally, depending on the final aging temperature (H900, H1025, H1075, etc.), the balance between strength, ductility, and toughness is adjusted according to the intended application.
In simple terms, the higher the final temperature, the greater its ductility and toughness, and the lower its hardness. For example, H900 provides maximum strength and hardness, with slightly reduced ductility, whereas H1025 offers a balance between the two, and H1150 maximizes ductilityand toughness while reducing its strength.
In some cases, an additional heat treatment is applied to optimize the resistance to stress corrosion cracking, particularly for high-temperature applications. To ensure dimensional accuracy and limit deformations, manufacturing operations (cutting, shaping, etc.) are generally performed after heat treatment.
Forming and Machining
15-5 PH is forged between 950 °C and 1180 °C and then air-cooled, which refines the grain. After welding, a solution treatment followed by aging is recommended to minimize residual stresses and preserve its mechanical properties.
It can be machined in either the hardened or solution-treated state, with saw cutting being preferred over thermal cutting to limit undesirable deformations and maintain a homogeneous structure. Mechanical cutting also allows direct transition to finishing machining (drilling, milling, turning) without the need to reheat the piece.
Applications
15-5 PH is used for components subjected to extreme conditions, whether in the civil or military sectors. Its use spans numerous industries: oil, gas, and marine, as well as chemical installations and paper manufacturing. It is particularly employed in the production of shafts, landing gear, valves, gears, fasteners, gas turbine components, and even nuclear reactor equipment. Its overall toughness plays a critical role in sectors where even the slightest cracking can have severe consequences.
Chemical composition of 15-5PH
The variations in its chemical composition for aerospace.
| % | C Carbon | Cr Chromium | Cu Copper | Mn Manganese | N Nitrogen | Nb Niobium | Ni Nickel | P Phosphorus | S Sulfur | Si Silicon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | <0.00 | 14.00 | 2.50 | <0.00 | <0.00 | 0.15 | 4.20 | <0.00 | <0.00 | 0.50 |
| Max. | 0.05 | 15.50 | 3.20 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 0.30 | 5.00 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 1.00 |
Related stainless steel alloys
17-4PH, 1.4548, UNS S17400, AMS 5643, AMS 5622, S17400
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET
17-7PH, S17700, 1.4568, AISI 631, X7CrNiAl17-7
SHEET
21-09-06, AMS 5561, Nitronic 40, S21900, X2CrMnNi21-6-9, Z4CMN 21-9-6
ROUND TUBE
AISI 301, Z12CN18-07, X12CrNi17-7, X10CrNi18-8
MOTHER COIL, COIL, SHEET
AISI 302, Z12CN18-09
SHEET
AISI 347, X6CrNiNb18-10, Z6CNNb18-11
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET, ROUND TUBE
AISI 431, X17CrNi16-2, Z15CN16-02, FE PM42, 1.4057, APX
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, SHEET
AISI 446
ROUND BAR
CALE PELABLE
SHEET
CUSTOM 465, MLX17, X1CrNiMoAlTi12-11
ROUND BAR
EZ100CD17
ROUND BAR
EZ12CNDV12
ROUND BAR
EZ15CN17-03
ROUND BAR
EZ1CNDAT12-09, MARVALX12, X1CrNiMoAlTi12-9
ROUND BAR
EZ2NKD18-8-5, MARAGING 250, X2NiCoMo18-8-5
RECTANGULAR BAR
EZ3NCT25, X3NiCrTi25
ROUND BAR, COIL, SHEET (THICKNESS > 6MM)
EZ6CND16-05-01
SQUARE BAR
EZ6NCT25, A286, X6NiCrTi25
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, WIRE, SHEET
EZ8CND17-04
ROUND BAR
GD223, X50NiMnCr12, Z50NMC12
ROUND BAR
PH13-8Mo, X3CrNiMoAl13-08-02, Z3CND13-08
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR
S130
ROUND BAR
S143
ROUND BAR
S143D
ROUND BAR
S144
ROUND BAR
S145
ROUND BAR
X12C13, X12Cr13, AISI 410, 1.4006, Z10C13
ROUND BAR, SHEET
X30Cr13, Z30C13
ROUND BAR
X6Cr17
ROUND BAR
X750
SHEET
Z100CD17
ROUND BAR
Z12CN13
SHEET
Z12CNDV12, JETHETE M152, X12CrNiMoV12
ROUND BAR, SHEET
Z25CNWS22
ROUND BAR
Z2CN18-10, AISI 304L, X1CrNi18-10
RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, WIRE, PROFILE, SHEET, PERFORATED SHEET, PVC SHEET, ROUND TUBE
Z6CND16-05-01, APX4, Z8CND17-04, X4CrNiMo16-5-1
ROUND BAR, SHEET
Z6CNT18-10, AISI 321, X6CrNiTi18-10, X6CNT18-10
SQUARE BAR, RECTANGULAR BAR, ROUND BAR, COIL, SHEET, ROUND TUBE
Key properties
The most remarkable properties of this stainless steel alloy
Ductility
≥ 3%
Tensile Strength
862–1552 MPa
Yield Strength
723.9–1172.1 MPa
Brinell Hardness
269–444 HB
How 15-5PH is used in aerospace
The practical applications of this stainless steel in aircraft construction.

Aircraft Flap Tracks
Airplane flaps, essential for takeoff and landing, are supported by flap tracks subjected to significant stresses. Stainless steel 15-5 PH is perfectly suited for these tracks due to its mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, and excellent corrosion resistance.
Fighter Jet Actuators
Actuators convert a signal into mechanical movement to control the aircraft’s moving parts. They can be manufactured from 15-5 PH, a material that ensures their reliability thanks to its strength, crack resistance, and durability.
Structural Components
15-5 PH is ideal for components exposed to high mechanical stresses and corrosion, such as structural parts of landing gear. It can be used in large sections while maintaining excellent mechanical properties.









